The Gulf of Mexico is one of the most iconic bodies of water in the United States, serving as a natural boundary between the southern states and Mexico. It is a bountiful ecosystem, rich in marine life and natural resources. Despite its significance, many people are not aware of the diverse habitats and life forms that call the Gulf home. In this article, we will take a deep dive into the Gulf of Mexico, exploring its geography, history, ecology, and culture.
Table of contents
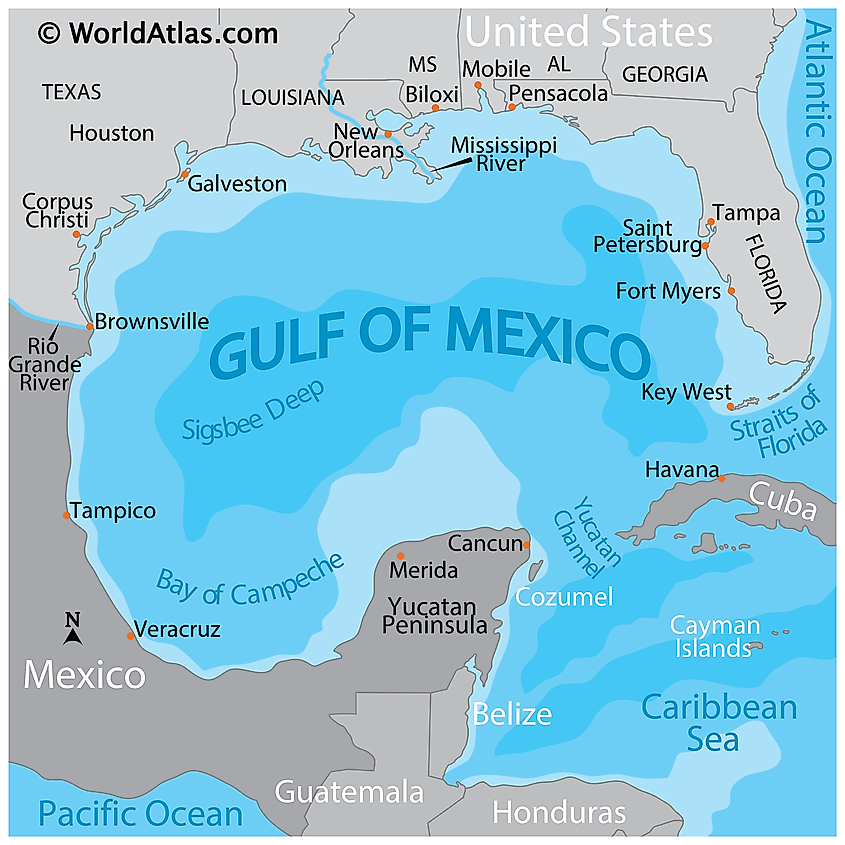
Geography of the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico is located in the southeastern region of North America, bordered by the United States to the north and west, Mexico to the east, and Cuba to the south. It is approximately 1,500 km (930 mi) wide and covers an area of about 1.6 million square km (600,000 square mi). The Gulf is connected to the Atlantic Ocean by the Florida Straits and the Yucatán Channel. It is one of the world’s largest marine ecosystems, with a maximum depth of 4,384 meters (14,383 feet).
The Gulf is home to many coastal states, including Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, and Florida. It is also an important shipping route, with numerous ports and harbors along its coastline. Additionally, the Gulf is home to many natural wonders, such as the Florida Keys, the Mississippi Delta, and the barrier islands of Alabama.
History of the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico has a rich history, dating back to the arrival of Native American tribes over 12,000 years ago. These tribes, such as the Tocobaga and the Calusa, were skilled fishermen and relied heavily on the Gulf for food and resources. The Gulf also played a significant role in the colonization of the Americas, as Spanish explorers such as Hernando de Soto and Álvar Núñez Cabeza de Vaca used the Gulf to navigate the continent.
In the 19th and early 20th centuries, the Gulf was a center of maritime trade and commerce. Cities such as New Orleans and Galveston became bustling ports, while the discovery of oil and gas in the Gulf spurred economic growth and development. However, this growth came at a cost, as overfishing, pollution, and other forms of human activity began to take their toll on the Gulf’s delicate ecosystem.
Ecology of the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico is home to a vast array of marine life, including over 15,000 species of plants and animals. Some of the most iconic species include dolphins, manatees, sea turtles, and a wide variety of fish and crustaceans. The Gulf is also home to many endangered and threatened species, such as the Kemp’s ridley sea turtle and the Gulf sturgeon.
One of the Gulf’s most unique features is its expansive system of coral reefs, which cover an area of over 600 square miles. These reefs are home to a diverse array of plant and animal species, including many that are not found anywhere else on Earth. Unfortunately, these reefs are under threat from climate change, ocean acidification, and other environmental pressures.
Culture of the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico has a rich cultural heritage, shaped by centuries of human activity and interaction. From the Native American tribes who first inhabited the Gulf coast to the diverse communities that call the region home today, the Gulf has been a center of trade, industry, and culture for thousands of years.
One of the most iconic cultural elements of the Gulf is its cuisine, which is renowned for its seafood dishes and bold flavors. Cities like New Orleans, Houston, and Mobile are known for their unique culinary traditions, which draw on the region’s diverse cultural influences.
The Gulf is also home to a vibrant music scene, with genres like jazz, blues, and country all having roots in the region. Festivals like the New Orleans Jazz & Heritage Festival and the Gulf Coast Jam bring together musicians and fans from all over the world to celebrate the Gulf’s rich musical heritage.
Challenges Facing the Gulf of Mexico
Despite its natural beauty and cultural significance, the Gulf of Mexico faces many challenges today. One of the most pressing issues is the impact of climate change and human activity on the Gulf’s delicate ecosystem. Rising temperatures and ocean acidification are threatening the Gulf’s coral reefs, while pollution and overfishing are putting many of the region’s fish and wildlife populations at risk.
Another major challenge facing the Gulf is the threat of oil spills and other environmental disasters. The Deepwater Horizon oil spill of 2010 was one of the largest environmental disasters in US history, releasing millions of barrels of oil into the Gulf and causing widespread damage to the ecosystem.
To address these challenges, many organizations and initiatives are working to promote conservation and sustainable use of the Gulf’s natural resources. Groups like the Gulf Restoration Network and the Gulf of Mexico Alliance are advocating for policies and practices that protect the Gulf’s ecosystems and support the communities that rely on them.
Conclusion
The Gulf of Mexico is a unique and complex ecosystem, shaped by centuries of human activity and natural processes. Its rich marine life, diverse cultural traditions, and economic significance make it an important part of America’s natural and cultural heritage. However, the Gulf also faces many challenges, from environmental degradation to the threat of oil spills and other disasters. By working together to protect and conserve this vital ecosystem, we can ensure that the Gulf of Mexico continues to provide for us and future generations to come.
Bibliography
- Gulf of Mexico Alliance. (2022). About the Gulf of Mexico. https://gulfofmexicoalliance.org/about-the-gulf/
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. (2022). Gulf of Mexico. https://oceanservice.noaa.gov/facts/gulf.html
- National Wildlife Federation. (2022). Gulf of Mexico. https://www.nwf.org/Educational-Resources/Wildlife-Guide/Threats-to-Wildlife/Gulf-of-Mexico
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. (2022). Gulf of Mexico Program. https://www.epa.gov/gulfofmexico


 For all latest articles, follow on Google News
For all latest articles, follow on Google News